An Overview of Positive and Negative Mode LCD Screens

Positive And Negative LCD Screens
LCD Screens are available in two options. Positive mode (dark letters on a light colored background) and negative mode (light colored letters on a darker background).
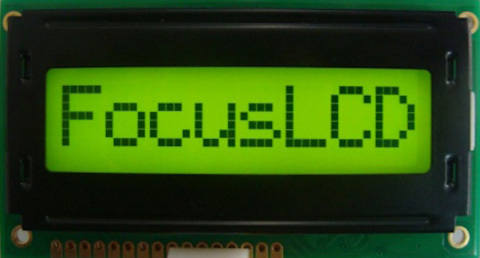
The photo below show a POSITIVE mode, STN yellow-green background with LED backlight
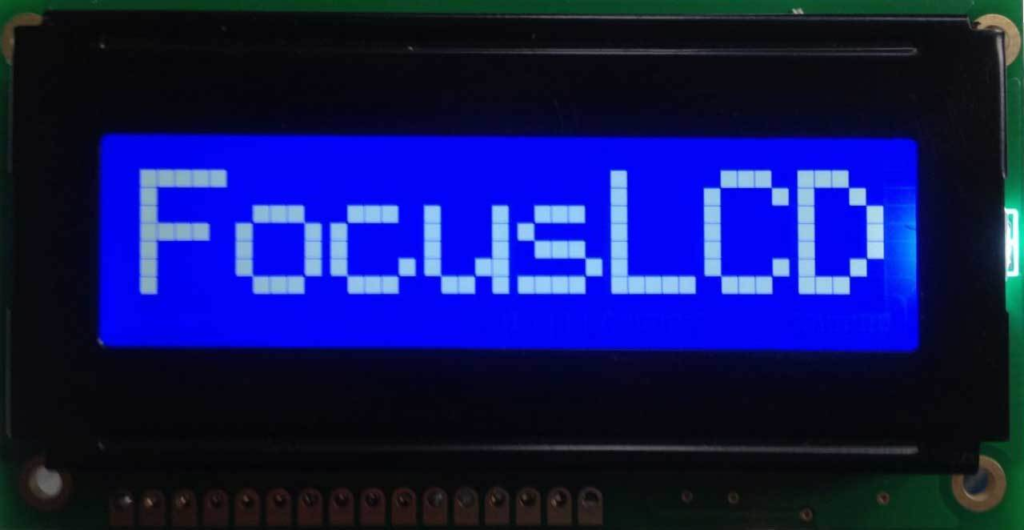
The photo below show a NEGATIVE mode, OLED black background with Blue characters
Positive mode is still more popular than negative mode, but negative mode is gaining ground and with the release of a new type of fluid technology called UWVD. UWVD is also known by BTN LCD screens. We believe that negative mode option will become even more popular as UWVD LCD technology moves into the main stream of LCD screens.
UWVD or Ultra-Wide Viewing Display Technology displays are a different approach to the older TN (Twisted Nematic), STN (Super Twisted Nematic) and FSTN (Film compensated Super Twisted Nematic) technologies. UWVD not only exceeds these technologies in contrast, but also offers a wider viewing angle.
Low power options for LCD screens
Negative mode LCD screens must have the backlight on to make the characters visible. This is true no matter if the display technology is TFT (Thin film transistor liquid crystal display), OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode), UWVD or monochrome. Backlights require much more power than the LCD modules. In fact, many times the backlight for the LCD screen display will require more power than all the other components combined.
This is a major consideration to take into account if your product is battery driven. If your product is battery powered and you need the negative mode LCD screen display, there are some options to help conserve power.
Dim the backlight after a few seconds of use. A dimmer LED backlight will require less current and will extend the life of the battery and the LEDs.
Turn off the backlight after a few seconds. This does not mean your product will shut off, just the backlight. This is very common with cell phones. The cell phone LCD screen will dim and then shut off even when you are talking on the phone.
Reduce the size of the display. The larger the display, the larger your backlight will need to be to make it readable. The larger the backlight, the more power required. You see this is some of the larger smart phones. The displays are very clear and sharp, but need to be recharged much more frequently.
Hot Spots on LCD screens
The two most popular colors for negative mode LCD screens are blue and white. The colors have only been around for a few years. They tend to be a bit more expensive than other colors such as yellow/green, Red, orange and others.
One set back to the blue and white LED’s is that the half-life of these colors is around 14K hours. Remember, half-life is not when the backlight burns out, but when it is half as bright as when it was first turned on.
If your application requires the backlight to be on 24/7, you may want to select a different color.
Another drawback to the blue and white LED’s when used as a backlight is that they can create hot spots. Hot spots are areas where the brightness of the backlight can be seen through the LCD glass. This creates a polka dot pattern.
One solution to avoid hot spots when using blue or white is to look at the new UWVD LCD screens.